Distributed estimation and data fusion in networked systems
Alain Kibangou ![]()
Hassen Fourati ![]()
Federica Garin ![]()
Aïda Makni ![]()
Distributed joint state and input estimation
Traditional analysis of linear average-consensus algorithms studies, for a given communication graph, the convergence rate, given by the essential spectral radius of the transition matrix (i.e., the second largest eigenvalues' modulus). For many graph families, such analysis predicts a performance which degrades when the number of agents grows, basically because spreading information across a larger graph requires a longer time; however, when considering other well-known quadratic performance indices (involving all the eigenvalues of the transition matrix), the scaling law with respect to the number of agents can be different. This is consistent with the fact that, in many applications, for example in estimation problems, it is natural to expect that a larger number of cooperating agents has a positive, not a negative effect on performance. It is natural to use a different performance measure when the algorithm is used for different purposes, e.g., within a distributed estimation or control algorithm. We are interested in evaluating the effect of the topology of the communication graph on performance, in particular for large-scale graphs.
Multi-sensors fusion in robotics
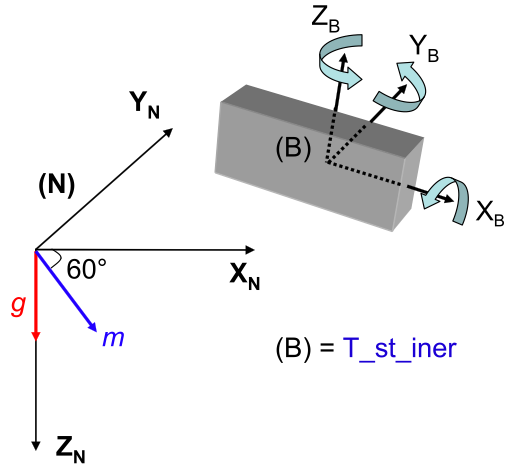
The coordinate system (B) of a rigid body represented in the Earth-fixed frame (N)
We are interested to motion capture (or attitude) of a body moving in 3D space by fusing inertial and magnetic sensors. In this context, the chosen attitude representation is the quaternion, and the available data are only from a triad of sensors including a 3-axis accelerometer, a 3-axis magnetometer and a 3-axis gyroscope (inertial measurement unit). Different approaches to estimate the quaternion from these data set were then proposed: the first is based on an additive non linear observer design and uses the quaternion addition technique for updating attitude estimates; the second and the third approaches propose, respectively, the design of a sliding mode observer and a complementary filter. The update of the estimates used in these last two approaches is based on quaternion multiplication; this technique shows that it is a good alternative to address this problem, and seems more appropriate for the quaternion algebra. The obtained results from both simulations and experimental studies (humans, robot, etc.) show the efficiency of these approaches to reconstruct the attitude with a good accuracy. The problem of attitude estimation is being studied in the case of aerial vehicles (hexa-rotors) with a strong focus on high acceleration movement.
Quadratic indices for performance evaluation of consensus algorithms
Traditional analysis of linear average-consensus algorithms studies, for a given communication graph, the convergence rate, given by the essential spectral radius of the transition matrix (i.e., the second largest eigenvalues' modulus). For many graph families, such analysis predicts a performance which degrades when the number of agents grows, basically because spreading information across a larger graph requires a longer time; however, when considering other well-known quadratic performance indices (involving all the eigenvalues of the transition matrix), the scaling law with respect to the number of agents can be different. This is consistent with the fact that, in many applications, for example in estimation problems, it is natural to expect that a larger number of cooperating agents has a positive, not a negative effect on performance. It is natural to use a different performance measure when the algorithm is used for different purposes, e.g., within a distributed estimation or control algorithm. We are interested in evaluating the effect of the topology of the communication graph on performance, in particular for large-scale graphs.
Selected papers
- H. Fourati, N. Manamanni, L. Afilal and Y. Handrich, Complementary observer for body segments motion capturing by inertial and magnetic sensors, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2013.
- H. Fourati, N. Manamanni, L. Afilal and Y. Handrich, Rigid body motions capturing by means of wearable inertial and magnetic MEMS sensors assembly: from the reconstitution of the posture toward the dead reckoning: an application in bio-logging, Novel Microelctronics: Technologies and Systems Applications, Taylor and Francis Books, 2012.
- F. Garin, D. Varagnolo and K. Johansson, Distributed estimation of diameter, radius and eccentricities in anonymous networks, 3rd IFAC Workshop on Distributed Estimation and Control in Networked Systems, 2012.
- A. Esna-Ashari Esfahani, A. Y. Kibangou and F. Garin, Distributed input and state estimation for linear discrete-time systems, IEEE 51st Conference on Decision and Control, 2012.
- A. Esna-Ashari Esfahani, F. Garin and A. Y. Kibangou, Joint input and state estimation for linear discrete-time networked systems, 3rd IFAC Workshop on Distributed Estimation and Control in Networked Systems, 2012.
- F. Garin and S. Zampieri, Mean square performance of consensus-based distributed estimation over regular geometric graphs, SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2012.
- A. Kibangou, Finite-time average consensus based protocol for distributed estimation over AWGN, IEEE 50th Conference on Decision and Control and European Control Conference, 2011.
- F. Garin, L. Schenato, A. Bemporad, M. Heemels and M. Johansson, A survey on distributed estimation and control applications using linear consensus algorithms, Networked Control Systems, Springer, 2011.
 Go to the full list of publications
Go to the full list of publications



















